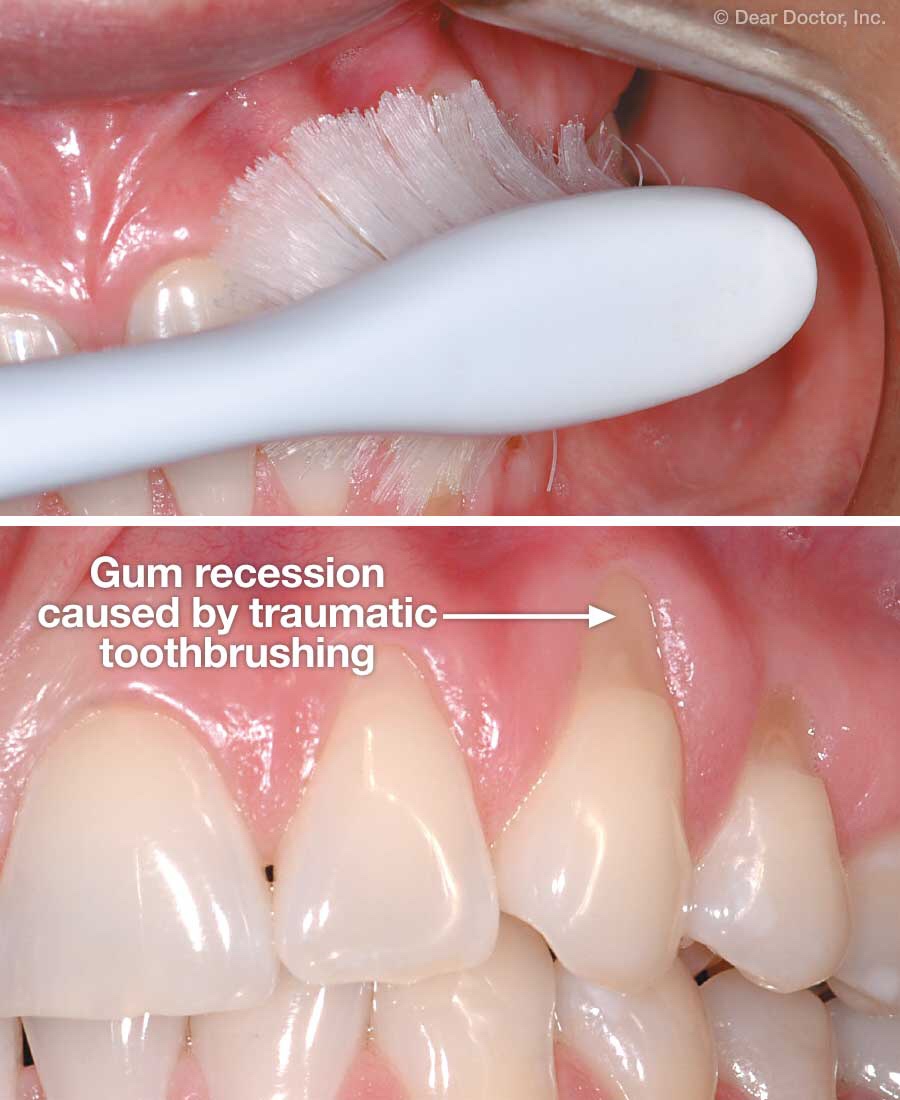
In simple words, Abrasion is loss of tooth structure due to foreign substances , like heavy brushing, hard bristels. Abrasion occours in the cervical region of tooth
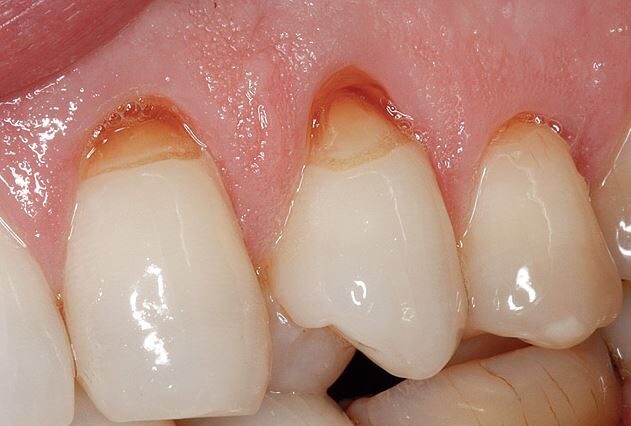
Etiology
- Faulty oral hygiene practice
- Horizontal brushing
- Excessive forces
- Quality of toothbrush
- pH and amount of dentifrice used
- Ill-fitting clasps of partial dentures cause localised abrasion lesions
- Fiction from toothpicks and interproximal brushes
- Tobacco Chewing
Treatment
We need to take careful consideration of aetiology and progression of the condition. That means, correct diagnosis is the prerequisite for the management of the lesion.
- If the lesion is localized and not interfering with the physiological function of the stomatognathic system = It may be restored
- If the abrasion is generalized and substantial = the habit should be discontinued and controlled
- If teeth are sensitive = use Flouride application
- If it’s class V lesion = Restoration with GIC
- If lesion involves a none conscious area in the posterior teeth = use metallic restorationon

No comments:
Post a Comment